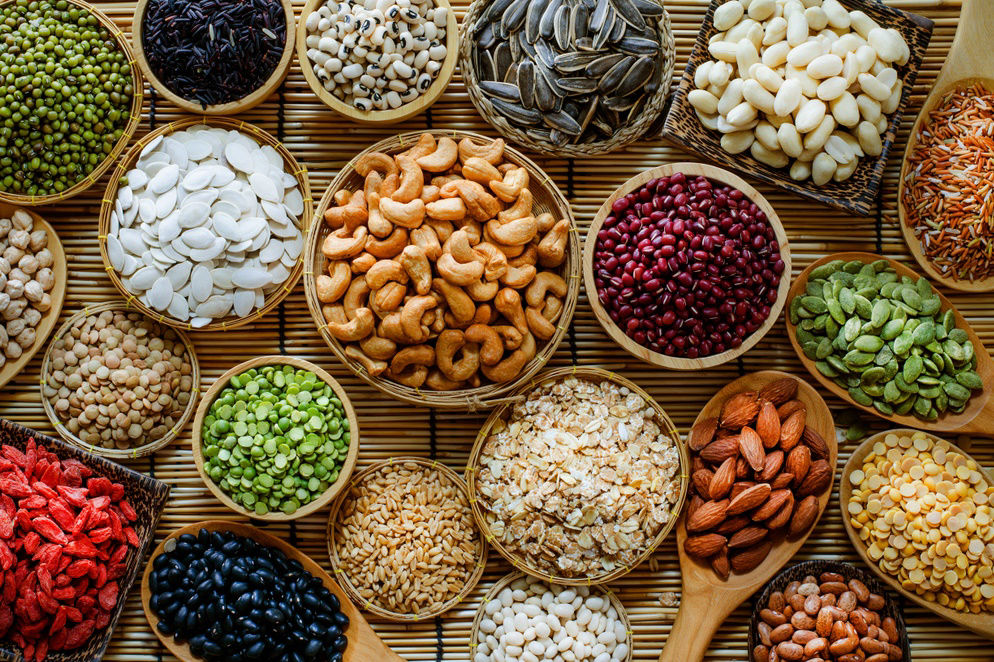
Instead of choosing sugary or fatty snacks, opt for nuts for a healthier choice as they are rich in fiber and protein. Although the fat content is relatively high, the fat they contain is a healthy type.
Studies have shown that nuts offer several health benefits – particularly in lowering the risk of heart disease.
Health Benefits of Nuts
Most of the fat content in nuts is monounsaturated fat, as well as omega-6 and omega-3 polyunsaturated fat. Nuts are also rich in vitamins and minerals such as vitamin E and magnesium.
Studies conducted on the health benefits of nuts have shown that those who eat nuts live longer as compared to those who do not. This is probably due to the benefits it provides to prevent a certain number of diseases (1,2,3). In addition, it has been found that diets that are high in nuts are not associated with weight gain or weight loss (4).
Nuts may also reduce the risk of high blood pressure and high cholesterol level in the blood (5, 6). Furthermore, eating nuts may lower the risk of certain cancers (7).
1. Almonds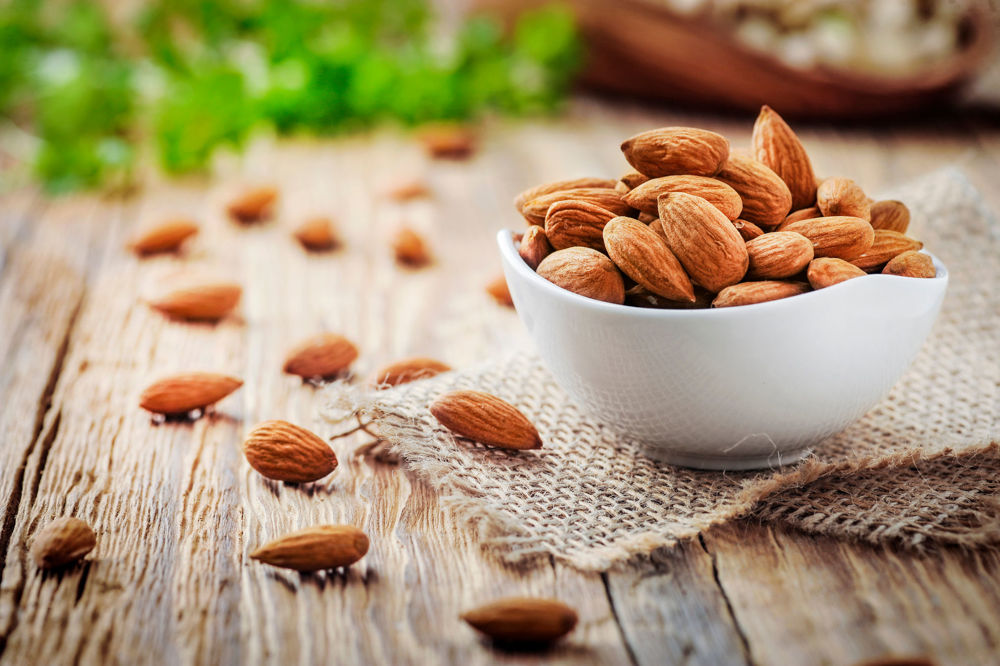
Almonds are one of the nuts rich in beneficial nutrients (8). Almonds have shown to reduce inflammation particularly in diabetes patients (9).
Additionally, almonds are beneficial in improving cholesterol levels in the blood (10). However, some studies revealed that there is insufficient evidence to support the statement.
2. Pistachios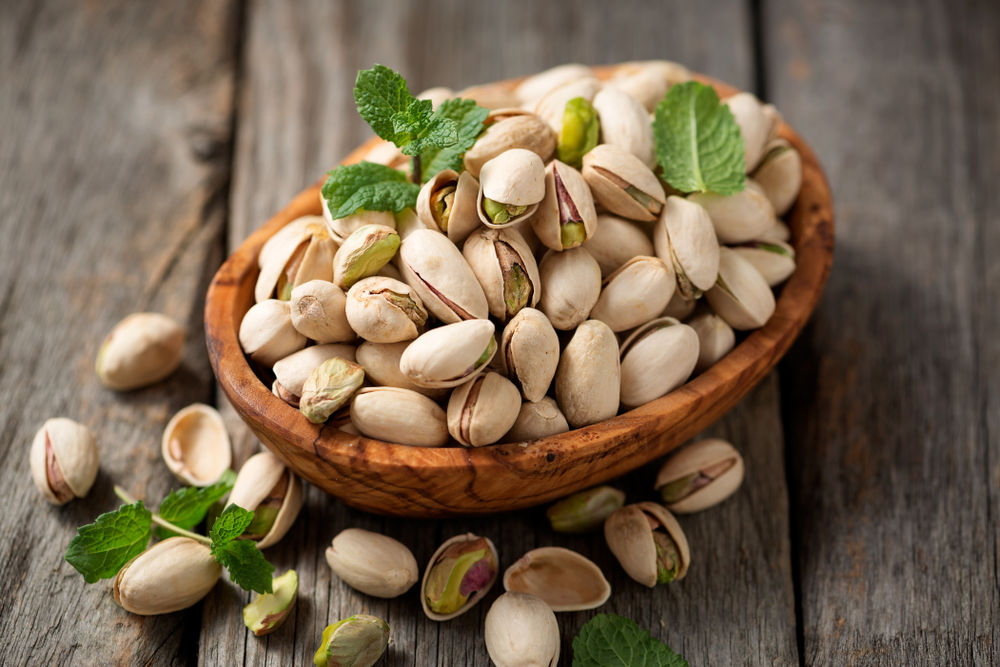
Pistachios are known as a nut that is rich in fiber (11).
Pistachios may help to reduce the risk of getting heart disease and high blood pressure. Studies have also shown that it may help to improve cholesterol levels in the blood (12).
3. Walnuts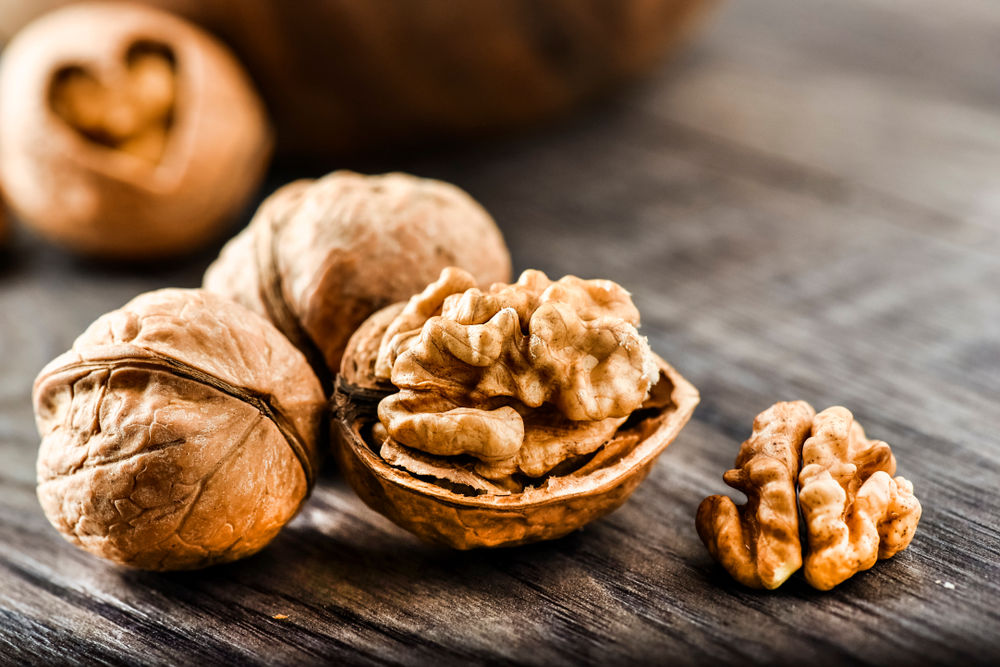
Walnut is a type of nut which contains rich sources of omega-3 fatty acid alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) (13).
They are famous for its anti-inflammatory properties and its ability to improve blood flow through the vessels (14, 15).
4. Hazelnuts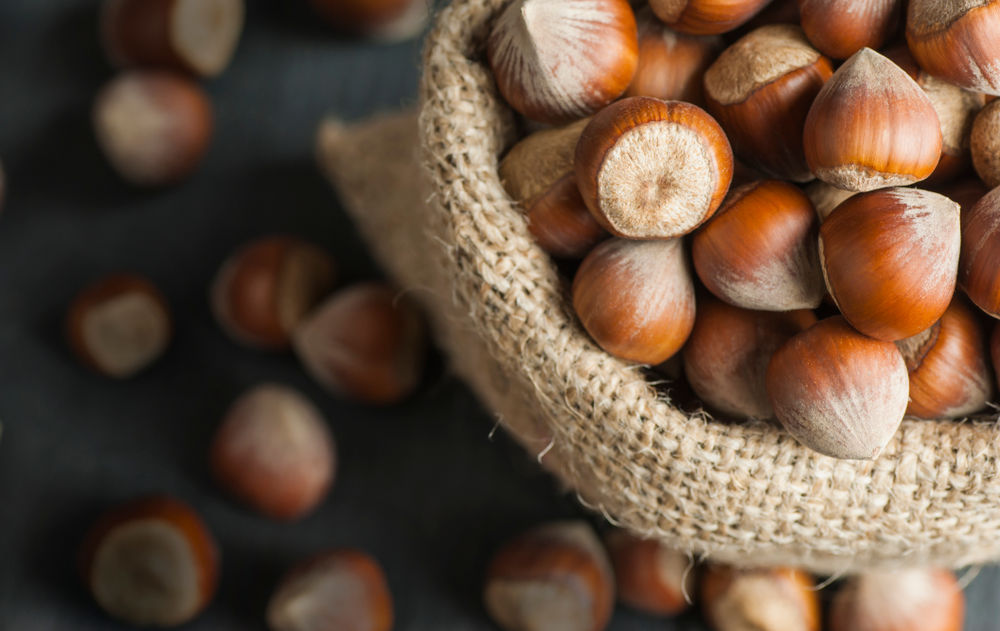
Hazelnuts are known as a nutritious nut (16).
Like other nuts, hazelnuts are beneficial in lowering the risk of heart disease and the cholesterol level in blood as well as in increasing the vitamin E level in the blood (17).
References:
1. van den Brandt, P. A., & Schouten, L. J. (2015). Relationship of tree nut, peanut and peanut butter intake with total and cause-specific mortality: A cohort study and meta-analysis. International Journal of Epidemiology. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyv039
2. Luo, C., Zhang, Y., Ding, Y., Shan, Z., Chen, S., Yu, M., … Liu, L. (2014). Nut consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and all-cause mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.113.076109
3. Bao, Y., Han, J., Hu, F. B., Giovannucci, E. L., Stampfer, M. J., Willett, W. C., & Fuchs, C. S. (2013). Association of nut consumption with total and cause-specific mortality. New England Journal of Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1307352
4. Flores-Mateo, G., Rojas-Rueda, D., Basora, J., Ros, E., & Salas-Salvadó, J. (2013). Nut intake and adiposity: Meta-analysis of clinical trials. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.111.031484
5. Djoussé, L., Rudich, T., & Gaziano, J. M. (2009). Nut consumption and risk of hypertension in US male physicians. Clinical Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2008.08.005
6. Sabaté, J., Oda, K., & Ros, E. (2010). Nut consumption and blood lipid levels: A pooled analysis of 25 intervention trials. Archives of Internal Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinternmed.2010.79
7 Viguiliouk, E., Kendall, C. W. C., Mejia, S. B., Cozma, A. I., Ha, V., Mirrahimi, A., … Sievenpiper, J. L. (2014). Effect of tree nuts on glycemic control in diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled dietary trials. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0103376
8. Nuts, almonds [Includes USDA commodity food A256, A264] Nutrition Facts & Calories. (n.d.). Retrieved November 20, 2019, from https://nutritiondata.self.com/facts/nut-and-seed-products/3085/2
9. Spiller, G. A., Miller, A., Olivera, K., Reynolds, J., Miller, B., Morse, S. J., … Farquhar, J. W. (2003). Effects of plant-based diets high in raw or roasted almonds, or roasted almond butter on serum lipoproteins in humans. Journal of the American College of Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2003.10719293
10. Liu, J. F., Liu, Y. H., Chen, C. M., Chang, W. H., & Chen, C. Y. O. (2013). The effect of almonds on inflammation and oxidative stress in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized crossover controlled feeding trial. European Journal of Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-012-0400-y
11. Nuts, pistachio nuts, raw Nutrition Facts & Calories. (n.d.). Retrieved November 20, 2019, from https://nutritiondata.self.com/facts/nut-and-seed-products/3135/2
12. Sheridan, M. J., Cooper, J. N., Erario, M., & Cheifetz, C. E. (2007). Pistachio nut consumption and serum lipid levels. Journal of the American College of Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2007.10719595
13. Nuts, walnuts, english [Includes USDA commodity food A259, A257] Nutrition Facts & Calories. (n.d.). Retrieved November 20, 2019, from https://nutritiondata.self.com/facts/nut-and-seed-products/3138/2
14. Chiang, Y. L., Haddad, E., Rajaram, S., Shavlik, D., & Sabaté, J. (2012). The effect of dietary walnuts compared to fatty fish on eicosanoids, cytokines, soluble endothelial adhesion molecules and lymphocyte subsets: A randomized, controlled crossover trial. Prostaglandins Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plefa.2012.07.007
15. Ma, Y., Njike, V. Y., Millet, J., Dutta, S., Doughty, K., Treu, J. A., & Katz, D. L. (2010). Effects of walnut consumption onendothelial function in type 2 diabetic subjects: A randomized controlled crossover trial. Diabetes Care. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc09-1156
16. Nuts, hazelnuts or filberts Nutrition Facts & Calories. (n.d.). Retrieved November 20, 2019, from https://nutritiondata.self.com/facts/nut-and-seed-products/3116/2
17. MercanlIgil, S. M., Arslan, P., Alasalvar, C., Okut, E., Akgül, E., PInar, A., … Shahidi, F. (2007). Effects of hazelnut-enriched diet on plasma cholesterol and lipoprotein profiles in hypercholesterolemic adult men. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602518
condition
Tips to Maintain a Healthy Digestive System
Monday, 10 February 2020
Do you know that it is important to have a healthy digestive system?















![[BUNDLE OF 2] Singlion Vitamin C + Lutein + Zinc Effervescent](https://www.vitasg.sg/images/thumbs/0002225_bundle-of-2-singlion-vitamin-c-lutein-zinc-effervescent_415.jpeg)



